In the world of SEO, Semantic SEO has emerged as a powerful approach to increase visibility by focusing on understanding search intent and the relationships between keywords. By optimizing content for semantic relevance rather than isolated keywords, websites can gain a competitive edge in search engine rankings.
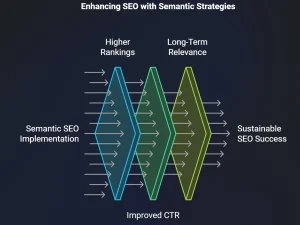
What is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO refers to the practice of creating content that responds directly to the broader context and intent behind user searches. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on exact-match keywords, Semantic SEO optimizes for related topics, subtopics, and concepts. This helps search engines better interpret content, enhancing its relevance for users.
Why Semantic SEO Matters:
- Enhances User Experience: By addressing the deeper needs behind search queries, Semantic SEO ensures that users find more meaningful answers.
- Improves Ranking Potential: Search engines reward content that provides complete, relevant responses, and this leads to higher rankings.
- Supports Long-Tail Keywords: Semantic SEO captures a variety of related search terms, allowing for greater visibility across diverse queries.
Key Strategies for Implementing Semantic SEO
To build a content strategy that ranks well and answers users’ needs, apply these fundamental Semantic SEO techniques:
1. Understand User Intent Deeply
Semantic SEO starts with understanding the search intent of users, categorized into three types:
- Informational – Users seek knowledge (e.g., “how to improve SEO”).
- Navigational – Users look for a specific website or page (e.g., “Backlink blog”).
- Transactional – Users intend to complete an action, such as a purchase (e.g., “buy SEO software”).
Tip: Conduct thorough research into what users want from a search term and align content to meet that exact intent.
2. Use Topic Clusters
Organize content into topic clusters where each post focuses on a specific subtopic, all interlinked to a main “pillar page.” This structure helps search engines recognize the depth and breadth of coverage on a subject.
- Example: If your pillar topic is “SEO,” subtopics could include “Keyword Research,” “On-Page SEO,” “Link Building,” etc.
- Benefit: Clusters allow you to cover related keywords and boost internal linking, enhancing search engine crawlers’ understanding of your site’s structure.
3. Optimize for Related Keywords and Synonyms
Search engines like Google now utilize natural language processing (NLP) to understand synonyms and related terms.
- Best Practice: Include synonyms and related phrases throughout your content to improve keyword diversity and relevance.
- Example: If optimizing for “content marketing,” incorporate related terms like “digital marketing,” “brand building,” and “online engagement.”
4. Leverage Structured Data
Structured data (e.g., schema markup) helps search engines interpret content contextually by adding metadata that clarifies the page’s meaning.
- Example: Using structured data for an FAQ section can help your answers appear directly in search results, improving click-through rates.
- Benefits: Enhanced SERP (Search Engine Results Page) features like rich snippets, knowledge panels, and video carousels.
5. Create In-Depth, Comprehensive Content
High-quality, well-researched content that thoroughly addresses a topic is central to Semantic SEO.
- Approach: Aim for depth by covering all aspects of a topic and providing value to the reader.
- Example: For a blog on “Link Building,” explain different techniques, tools, pros and cons, and case studies.
- Tip: Answer potential follow-up questions in the same piece, enhancing your content’s completeness.
6. Use Internal Linking to Signal Topic Relevance
Strategically place internal links between related pieces of content to establish authority and relevance within your site.
- Benefits: This approach distributes link equity, helping search engines understand topic relationships.
- Example: Link your content on “SEO Basics” to an article on “Advanced SEO Techniques” to create a logical knowledge flow.
7. Focus on Entity-Based SEO
Entities (distinct concepts recognized by search engines) include people, places, brands, and products. Content that clarifies entities aids Semantic SEO, helping Google understand the connections between them.
- Example: When writing about “iPhone,” mention related entities like “Apple,” “smartphone,” “iOS,” and “App Store” to enhance context.
- Benefits: Entity-focused content increases relevance for various related searches, helping improve visibility in niche areas.
Tools to Enhance Your Semantic SEO Strategy
- Google’s Natural Language API: Analyzes text to help you understand how Google interprets entities in your content.
- LSIGraph: Generates LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords to enrich your content with relevant phrases.
- SurferSEO and Clearscope: SEO tools that provide semantic keyword suggestions based on top-ranking pages, helping align your content with user intent.
How Semantic SEO Complies with Google’s EEAT Guidelines
- Experience: Demonstrate in-depth expertise on topics with research-backed information.
- Expertise: Establish authority with well-researched, comprehensive content.
- Authoritativeness: Cite reputable sources and provide factual information to increase credibility.
- Trustworthiness: Ensure accuracy, transparency, and professionalism across all content.
Benefits of Implementing Semantic SEO
- Higher Rankings: Semantic SEO aligns with how search engines rank for relevancy, boosting your page’s chances of ranking higher.
- Improved Click-Through Rates (CTR): With schema markup and rich snippets, semantic-optimized pages can stand out more in SERPs.
- Long-Term Relevance: By focusing on intent rather than single keywords, Semantic SEO builds a future-proof content strategy adaptable to algorithm changes.
Conclusion
Semantic SEO is not merely about optimizing for search engines but creating user-centered, high-quality content that comprehensively addresses topics. By applying these strategies, businesses can increase their authority, relevance, and ranking potential, meeting both user needs and search engine criteria.
Quick Tips Recap
- Understand User Intent: Focus on what users truly want from a query.
- Build Topic Clusters: Organize content around central themes.
- Use Synonyms and Related Terms: Diversify keyword usage.
- Add Structured Data: Make content easier for search engines to understand.
- Prioritize Quality and Depth: Cover topics thoroughly to build authority.